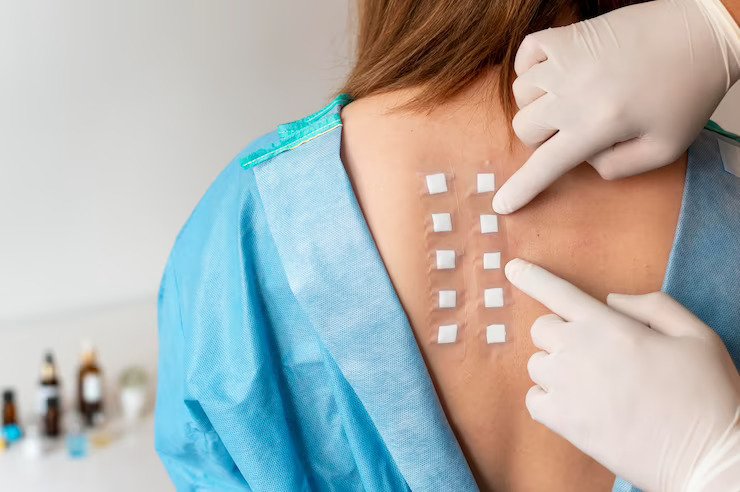
Welcome to a new topic today. We’re discussing dermatological allergy testing. This simple, yet effective procedure is often overlooked in managing allergy symptoms. We base our conversation on the expertise of angela azar, md, pc. She has made remarkable strides in this field. Her work has shown that identifying allergens can dramatically improve quality of life. It can halt uncomfortable allergic reactions before they even start. Today, we’re diving deep into the benefits of this vital procedure.
The Process of Dermatological Allergy Testing
The process is simple. The skin is gently pricked or scratched with a tiny amount of an allergen. This is usually done on the forearm or back. The skin’s reaction is then observed for any signs of an allergic response.
Quick Results
One of the key benefits of dermatological allergy testing is the speed at which results are obtained. In most cases, you will know within 20 minutes if you have an allergy. This is significantly quicker than blood tests, which can take a few days to get results.
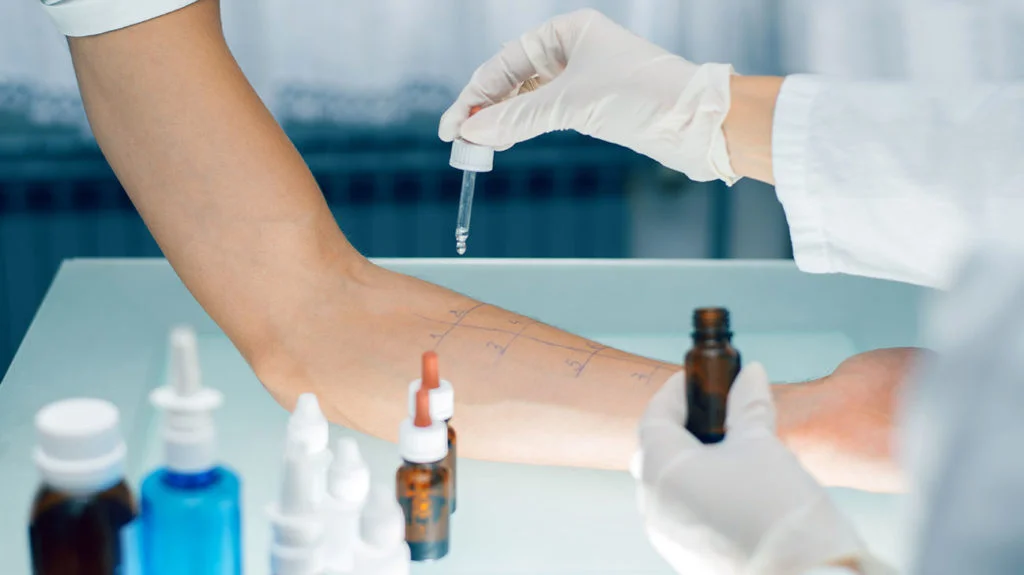
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of allergies can prevent severe allergic reactions. Knowing what you’re allergic to can help you avoid those allergens. This can lead to a better quality of life. You can learn how to manage your condition with guidance from a healthcare professional.
The Power of Knowledge
Knowledge is power. Identifying allergens gives you the power to prevent uncomfortable and potentially dangerous allergic reactions. You can make informed decisions about your diet and lifestyle.
Comparison of Allergy Testing Methods
| METHOD | TIME FOR RESULTS | ACCURACY | COMFORT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dermatological Allergy Testing | 20 minutes | High | Minor discomfort |
| Blood Allergy Testing | Several days | High | No discomfort |
Dermatological allergy testing is a powerful tool. It allows for the identification and management of allergens. This can significantly improve the quality of life. For further information, you may refer to National Institutes of Health.